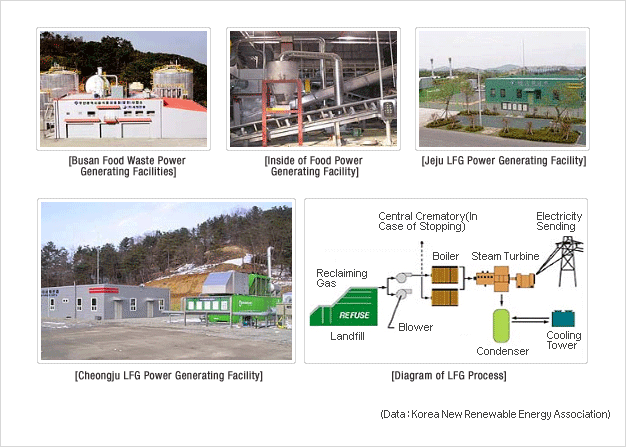
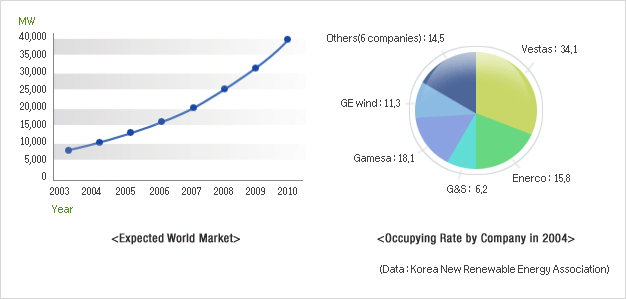
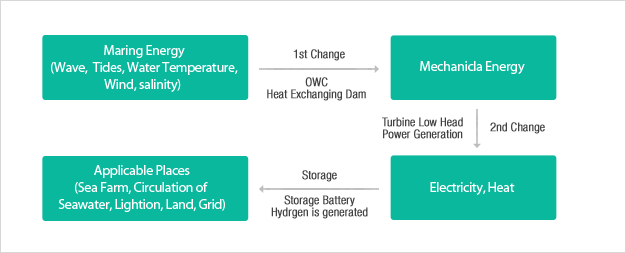
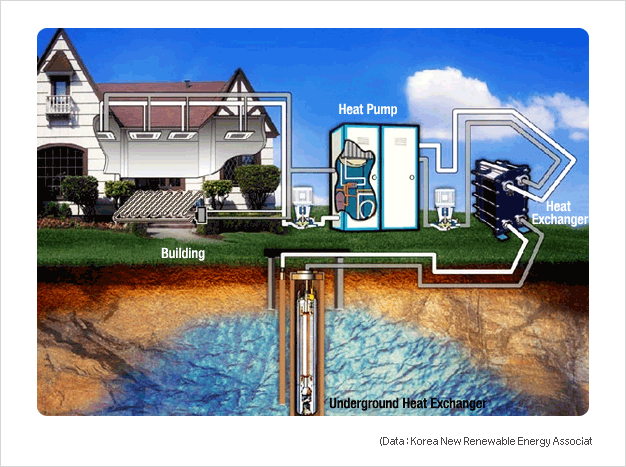
- Development of high efficient
- Eco-friendly technology reducing SOx and NOx to more than 95% and 90%, respectively
- Making various fuels of low quality(coal, intermediates, waste, etc) into the energy of high quality
|
- As the composition of equipment and its controlling is complicated, optimization of design, high efficiency and low cost are required
- As necessary area is broad, the equipments are large and the cost of systems are expensive, only a few of large companies can develop them
|